Electronic Signature Formats and Examples
Table of contents
- 4 main electronic signature formats
- Other types of signature formats
- Benefits of adopting electronic signatures
- E-signature formats and examples in summary
-
About Concord
Effortless contract management, from drafting to e-signing and beyond. Book a live demo to see Concord in action.
Request demo
In the fast-paced, ever-evolving digital landscape, the adoption of an electronic signature format is no longer an option but a necessity. In the United States, the ESIGN Act, also known as the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act, has established the legal recognition of electronic signatures. Similar laws have also been introduced all over the world.
These regulations recognize various electronic signature formats as legally binding, effectively bringing an end to the time-consuming and often impractical tradition of obtaining a handwritten signature.
4 main electronic signature formats
Electronic signatures have brought a level of flexibility and accessibility unheard of in the age of pen and ink. However, not all electronic signatures are created equal.
There are four main formats of electronic signatures:
- Typewritten e-signatures
- Scanned image electronic signatures
- Clickwrap signatures
- Digitized signature pad
Each format is specifically tailored to cater to different contexts, ensuring security, validity, and, above all, convenience. Let’s explore some of the common e-signature types.
Format 1: Typewritten e-signatures
The typewritten electronic signature format allows a signer to type their name onto a signature line in an electronic document, indicating their approval or consent.
Despite its simplicity, this type of electronic signature is legally binding under many laws, e.g. the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act, presenting a quick and easy alternative when the signer’s physical presence isn’t feasible.
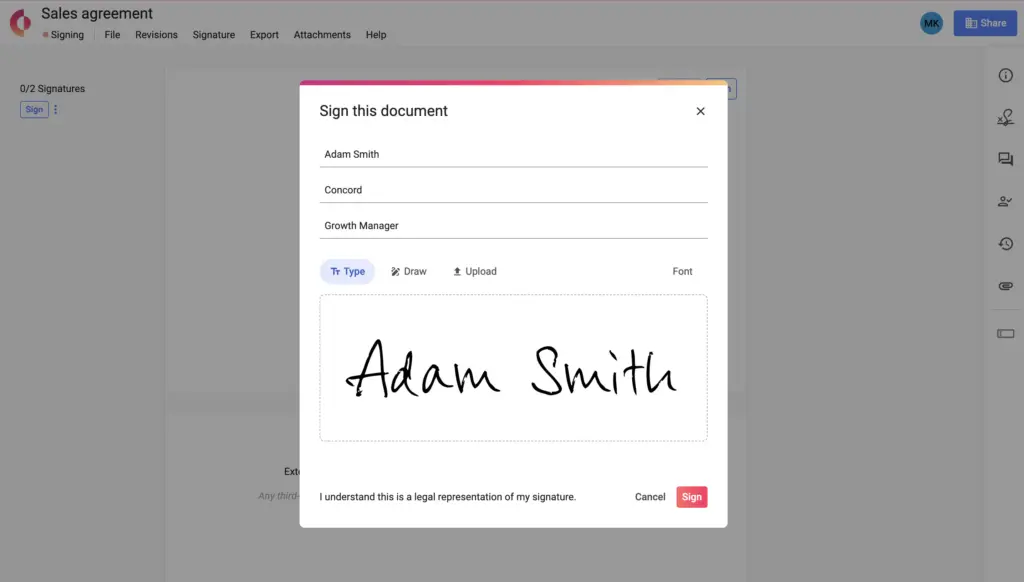
Typewritten e-signature example
As you can see in the image of Concord software below, this format is often one of the ways to sign a document inside a CLM or e-signature tool. Therefore, this electronic signature type can be used for a wide variety of digital contracts, from employment contracts, through NDAs, to vendor agreements, and much more.
Format 2: Scanned image
The scanned image format involves a signer signing on paper, scanning the signed document, and then attaching it to an electronic document. While it may seem slightly time-consuming compared to other methods, it resembles a traditional handwritten signature, which can be preferable in certain scenarios.
Scanned image signature example
For instance, let’s consider the scenario of signing a contract remotely. You can sign your name on a blank piece of paper, scan it using a smartphone scanner app, and then upload the scanned image of your signature to the electronic document. This method retains the personal touch of your signature, and despite the extra steps, provides a balance between the traditional and digital realms.

Format 3: Clickwrap signature
For anyone who has ever clicked an “I Agree” button or ticked a checkbox on an online form, you’ve used a clickwrap signature. This electronic signature format is popular in online agreements due to its simplicity and ease of implementation on digital platforms.
Clickwrap signature example
Take, for example, the process of creating a new email account. During the sign-up phase, you’re often presented with a Terms of Service agreement. By ticking a checkbox or clicking a button labeled “I Agree” or “Accept Terms,” you’re using a clickwrap signature to affirm your consent to the terms outlined, effectively signing the agreement electronically.

Format 4: Digitized signature pad
Using a digitized signature pad, the signer physically signs on a digital device, and this signature is then captured and embedded in the document. This format can provide an enhanced level of authenticity and security because it involves unique biometrics of the signer.
Digitized signature pad example
A good example of this is the medical sector where doctors often use a digitized signature pad for signing electronic healthcare contracts and medical records. When prescribing medication or submitting medical notes, the doctor signs using a stylus on a digitized pad. This signature is then captured and attached to the electronic document, ensuring the records are securely authorized by the appropriate medical professional.

Other types of signature formats
Alongside these electronic signature formats, there are also other forms of signatures that provide unique advantages.
Digital signature
A digital signature is different from an electronic signature, as it is a more advanced type that uses cryptography for enhanced security. This signature format involves a signer’s private key, known only to them, which is used to encrypt data.
The recipient uses the public key in the signer’s digital certificate to decrypt the data, thus verifying its authenticity. If the information is successfully decrypted, it validates the authenticity of both the signature and digital signature, ensuring the integrity of the signed document.
Wet signature
Despite the digital revolution, the conventional “wet signature”, or a traditional handwritten signature, retains its place. There’s an undeniable psychological impact of physically signing a document that some find hard to let go of, especially in high-stakes scenarios.
However, with the many benefits of electronic signatures such as convenience and security, the use of wet signatures is on the decline.
Benefits of adopting electronic signatures
Adopting electronic signatures extends beyond simply digitizing a traditional process, as it:
- eliminates the need for physical contract storage,
- reduces the risk of losing important documents,
- simplifies the process of obtaining multiple signatures,
- accelerates the turnaround time of document processing, thereby increasing efficiency.
E-signature formats and examples in summary
The evolution of the signature, from its ink and paper origins to the many electronic formats we see today, has revolutionized how we handle agreements. Whether you choose to use a typewritten name, a scanned image of your handwritten signature, or a digital signature backed by a public key, depends largely on the needs of your specific situation.
In the age of digital transformation, where efficiency is king, understanding the formats and types of electronic signatures is no longer optional. Remember that the law is on your side: regulations such as the ESIGN Act have ensured that your electronic signatures are legally binding and that they carry the same weight as their pen-and-paper predecessors.
Navigating this new world might seem daunting, but with a bit of knowledge, the benefits of this technological revolution are well within your grasp. And remember, the easiest way to get e-signatures on contracts is with an all-in-one contract automation too.




